Lung Cancer CT Scan: A Comprehensive Guide for Detection and Treatment
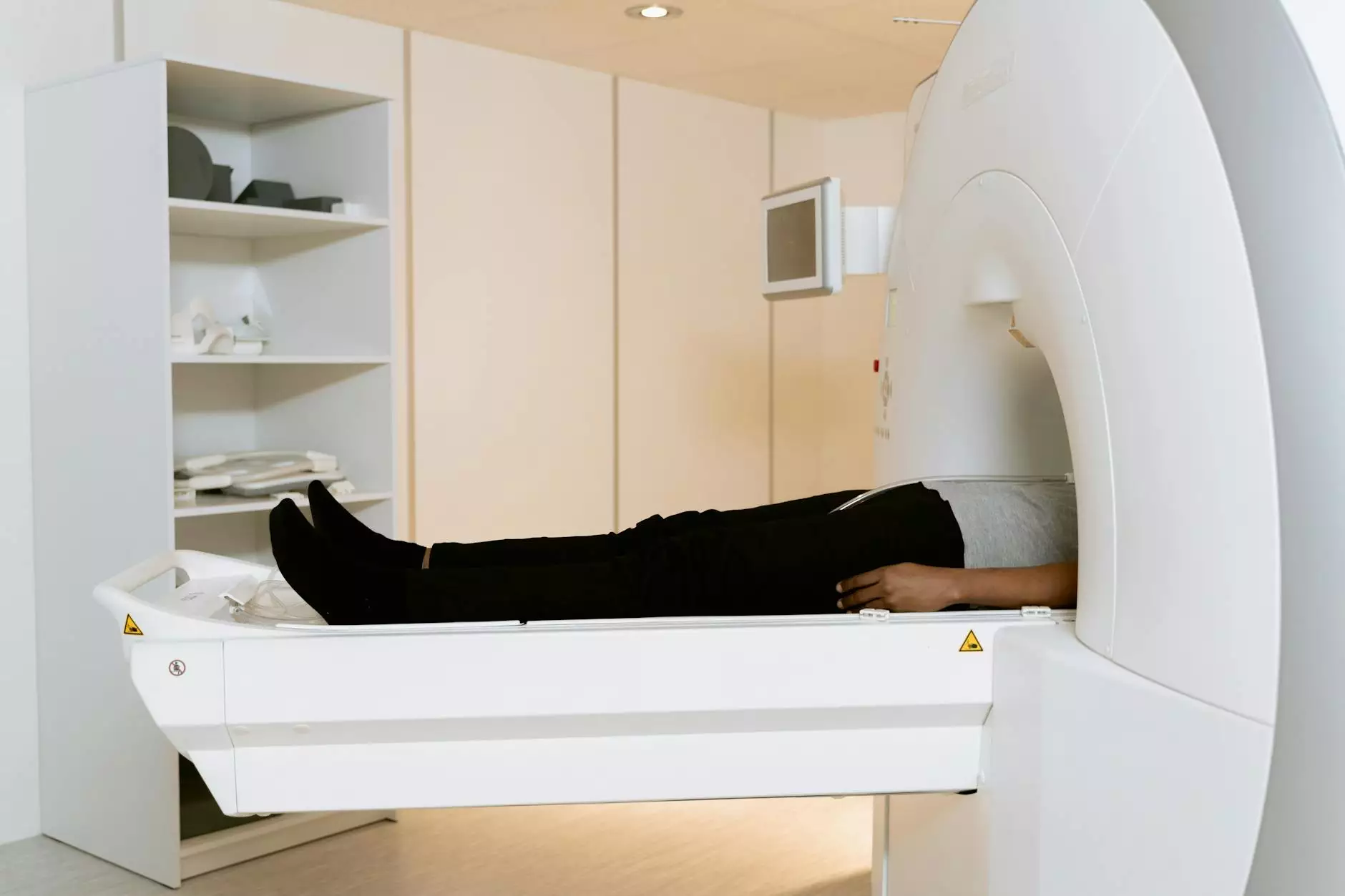
Lung cancer is among the leading causes of cancer-related deaths worldwide. Early detection plays a crucial role in improving treatment outcomes and enhancing survival rates. One of the most effective diagnostic tools for identifying lung cancer is a lung cancer CT scan. This article will explore the significance of lung cancer CT scans, how they work, and their role in effective treatment plans.
What is a Lung Cancer CT Scan?
A CT (computed tomography) scan, also known as a CAT scan, utilizes a series of X-ray images taken from different angles around the body, processed by a computer to create cross-sectional images of bones, blood vessels, and soft tissues. When it comes to lung cancer, these scans provide detailed images of the lungs, enabling physicians to detect abnormalities or early signs of cancer.
Why Choose a CT Scan for Lung Cancer Detection?
- High Accuracy: CT scans provide more detailed images than standard X-rays, allowing for early detection of lung nodules and tumors.
- Non-Invasive: The process is relatively quick, painless, and does not require any invasive procedures.
- Detailed Analysis: Radiologists can view cross-sectional images, making it easier to identify the exact location and size of lesions.
- Guidance for Further Testing: Abnormal findings on a CT scan often lead to further testing, such as biopsies, which are crucial for accurate diagnosis.
How Does a Lung Cancer CT Scan Work?
The process of a lung cancer CT scan is straightforward. Here’s an overview of what you can expect:
- Preparation: You may be asked to avoid eating or drinking for a few hours before the scan. Inform your healthcare provider if you have any allergies, especially to contrast materials.
- During the Scan: You will lie on a narrow examination table that slides into the CT scanner. You might need to hold your breath for a few seconds while the images are being taken. The whole process usually takes about 10 to 30 minutes.
- Post-Scanning: After the scan, you can resume your normal activities immediately. The results will be evaluated by a radiologist and shared with your physician for further discussion.
Understanding CT Scan Results
The interpretation of lung cancer CT scan results can be complex. Radiologists analyze the images for any signs of disease, including:
- Size and Shape of Nodules: The presence of nodules can indicate potential tumors; their size and growth patterns help determine if they are likely malignant.
- Location: Tumors located in certain areas may indicate specific types of lung cancer.
- Surrounding Tissues: The scan can reveal whether cancer has invaded nearby tissues or lymph nodes.
The Role of Lung Cancer CT Scans in Treatment Planning
Once a diagnosis of lung cancer is confirmed, the findings from the CT scans play a significant role in formulating an effective treatment plan. Here are some key contributions:
- Staging the Cancer: CT scans help to determine the stage of lung cancer, which is crucial for planning treatment options and predicting outcomes.
- Surgical Planning: For patients undergoing surgery, CT images help surgeons visualize the tumor’s relation to surrounding structures.
- Monitoring Treatment Responses: After initiating treatment, follow-up CT scans can assess how well the cancer is responding, helping to adjust therapies if necessary.
Potential Risks of CT Scans
While CT scans are invaluable diagnostic tools, they do come with certain risks. Notably:
- Radiation Exposure: CT scans involve exposure to a dose of ionizing radiation. However, the benefits often outweigh the risks, especially when monitoring lung cancer.
- Allergic Reactions: Some patients may have allergic reactions to contrast dye used in certain CT scans.
Alternatives to CT Scans
Though CT scans are powerful diagnostic tools, there are alternative methods for lung cancer screening and diagnosis:
- X-rays: Standard chest X-rays can detect larger tumors but are less sensitive than CT scans for early detection.
- Bronchoscopy: This invasive procedure involves using a camera to examine the lungs and collect samples.
- Biopsies: Tissue samples can be taken from suspicious areas for laboratory testing to determine the presence of cancer cells.
Conclusion: The Importance of Timely Lung Cancer CT Scans
In conclusion, early detection is crucial in the fight against lung cancer. The role of a lung cancer CT scan cannot be overstated, as it facilitates early diagnosis, guides treatment plans, and improves patient outcomes. For residents in Singapore, HelloPhysio.sg provides access to the latest diagnostic tools and personalized care. Schedule your consultation today to take the first step towards a healthier future.
FAQs about Lung Cancer CT Scans
1. How often should I get a lung cancer CT scan?
The frequency of CT scans depends on various factors, including risk profile and previous findings. High-risk patients may require annual screening, while others might need scans based on clinical indications.
2. What should I do if I receive abnormal CT scan results?
If you receive abnormal results, consult your healthcare provider to discuss further diagnostic steps and potential treatment options. Early action is crucial.
3. Are CT scans painful?
No, CT scans are non-invasive and generally painless. Some patients may experience mild discomfort or anxiety lying still for the duration of the scan.
4. Can a CT scan cure lung cancer?
A CT scan itself cannot cure cancer; however, it is an essential diagnostic step that aids in the early detection and management of lung cancer, leading to more effective treatment options.
For more information about lung cancer CT scans and other healthcare services, visit HelloPhysio.sg.